Azelaic Acid for Rosacea: What It Is and How It Works
When dealing with Azelaic Acid, a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid derived from grains, known for its antibacterial and anti‑inflammatory properties. Also called dihydroxy‑benzene‑carboxylic acid, it is widely used in dermatology to calm redness, reduce papules, and even out skin tone. azelaic acid rosacea has become a go‑to option for many because it targets the root causes of flare‑ups without the harsh side effects of some prescription drugs.
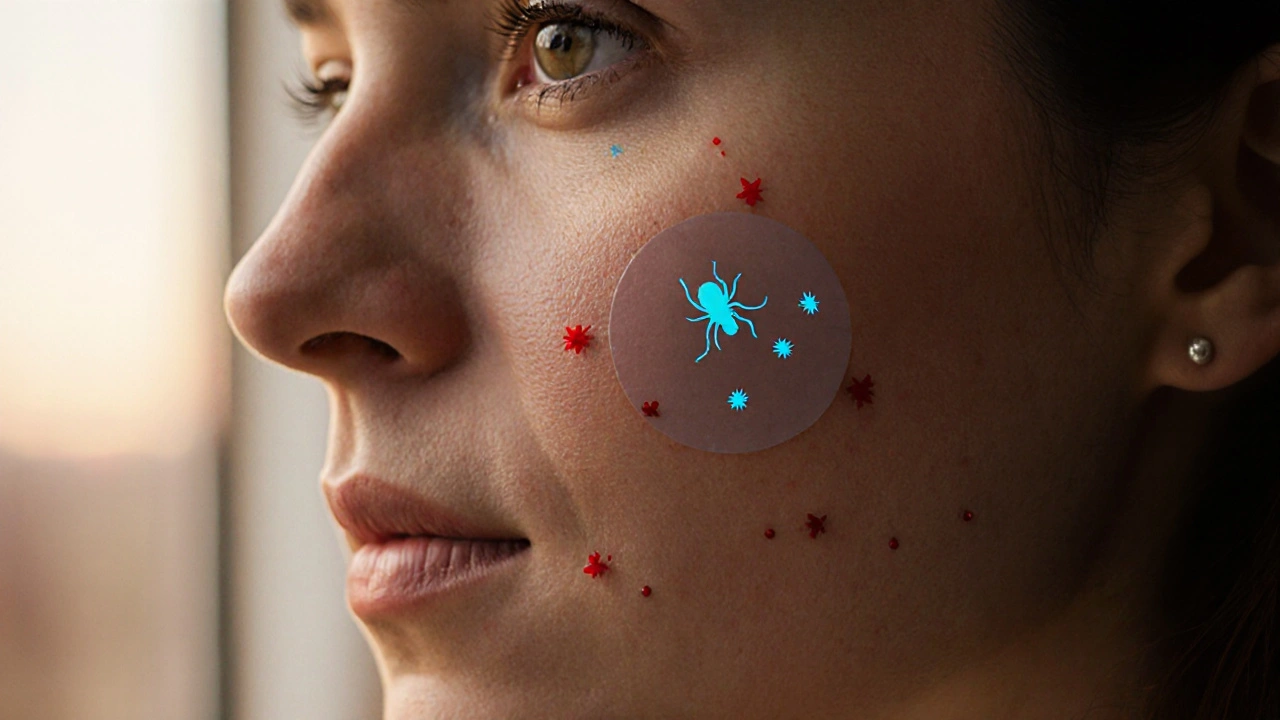
Rosacea itself is a chronic skin condition that shows up as persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne‑like bumps. Rosacea, an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the central face, often worsens with heat, stress, or certain foods. Because the skin barrier in rosacea patients is usually compromised, gentle yet effective ingredients become essential. That’s where topical therapies step in. Topical Treatment, any medication applied directly to the skin, such as creams, gels, or lotions, designed to deliver active ingredients where they’re needed most. Azelaic acid fits perfectly into this category because it can be formulated in low‑irritation gels or creams that soothe while they treat.
Using azelaic acid for rosacea creates a clear semantic chain: the condition (Rosacea) requires gentle, anti‑inflammatory care (Topical Treatment), and azelaic acid provides that care by reducing skin inflammation and normalizing the skin barrier. Research shows that a 15‑20% azelaic acid formulation can cut redness by up to 30% after just four weeks, and it also helps fade post‑inflammatory hyperpigmentation—a common complaint for rosacea sufferers. The acid works by inhibiting the growth of *Propionibacterium acnes* and *Demodex* mites, both of which can aggravate flare‑ups, while simultaneously calming the immune response that leads to flushing.
How to Choose and Use Azelaic Acid Effectively
First, look for products that list azelaic acid as the main active ingredient and contain a concentration of 15% or higher for therapeutic use. Avoid formulas packed with fragrances or alcohol, as those can break down the skin barrier further. Apply a thin layer once or twice daily after cleansing, ideally on dry skin to minimize irritation. Start with a short routine—apply every other night—and increase frequency as tolerated. Pair the acid with a gentle moisturizer that contains ceramides or hyaluronic acid; this reinforces the skin barrier and locks in moisture.
It’s also smart to consider complementary skincare habits that support azelaic acid’s action. Sunscreen is non‑negotiable because UV exposure spikes rosacea symptoms and can degrade the acid over time. Choose a mineral‑based SPF with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which are less likely to irritate sensitive skin. Additionally, keep a diary of triggers—spicy foods, hot drinks, extreme temperatures—and adjust lifestyle choices accordingly. By combining azelaic acid with a tailored routine, you create a holistic approach that addresses both the visible redness and the underlying inflammation.
Beyond azelaic acid, other topical tools often appear in rosacea management plans, such as metronidazole or ivermectin creams. These agents each target different pathways: metronidazole reduces bacterial load, while ivermectin tackles *Demodex* mites. Understanding how each fits into the broader treatment landscape helps you and your dermatologist craft a personalized regimen. Azelaic acid often serves as a bridge between prescription‑only options and over‑the‑counter gentle care, making it a versatile choice for many skin types.
For those who wonder whether azelaic acid can also help with acne‑related rosacea breakouts, the answer is yes. Its keratolytic action helps unclog pores, while its anti‑bacterial effect curbs the bacteria that contribute to both acne and rosacea. This dual benefit means you can simplify your skincare shelf by consolidating products, reducing the chance of mixing incompatible actives.
In practice, the best results come from consistency. Most users notice a calming effect within the first two weeks, but the full benefits—especially on pigmentation—often take six to eight weeks. Patience and regular use are key, as with any skin‑care routine.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive deeper into buying safe medications online, managing skin inflammation, and practical tips for rosacea‑related concerns. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to fine‑tune an existing regimen, the collection offers real‑world advice you can apply right away.
Soolantra (Ivermectin) vs Other Rosacea Treatments: Pros, Cons & Best Choice
A detailed side‑by‑side comparison of Soolantra (ivermectin) with other rosacea treatments, covering efficacy, side effects, cost and how to choose the right option.
Read